Tube Bending
Tube bending is a metal forming process used to create curved or bent shapes in cylindrical tubes or pipes. It involves applying controlled forces to the tube to deform it permanently and achieve the desired bend radius and angle. Tube bending is widely used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, plumbing, HVAC, and furniture manufacturing.
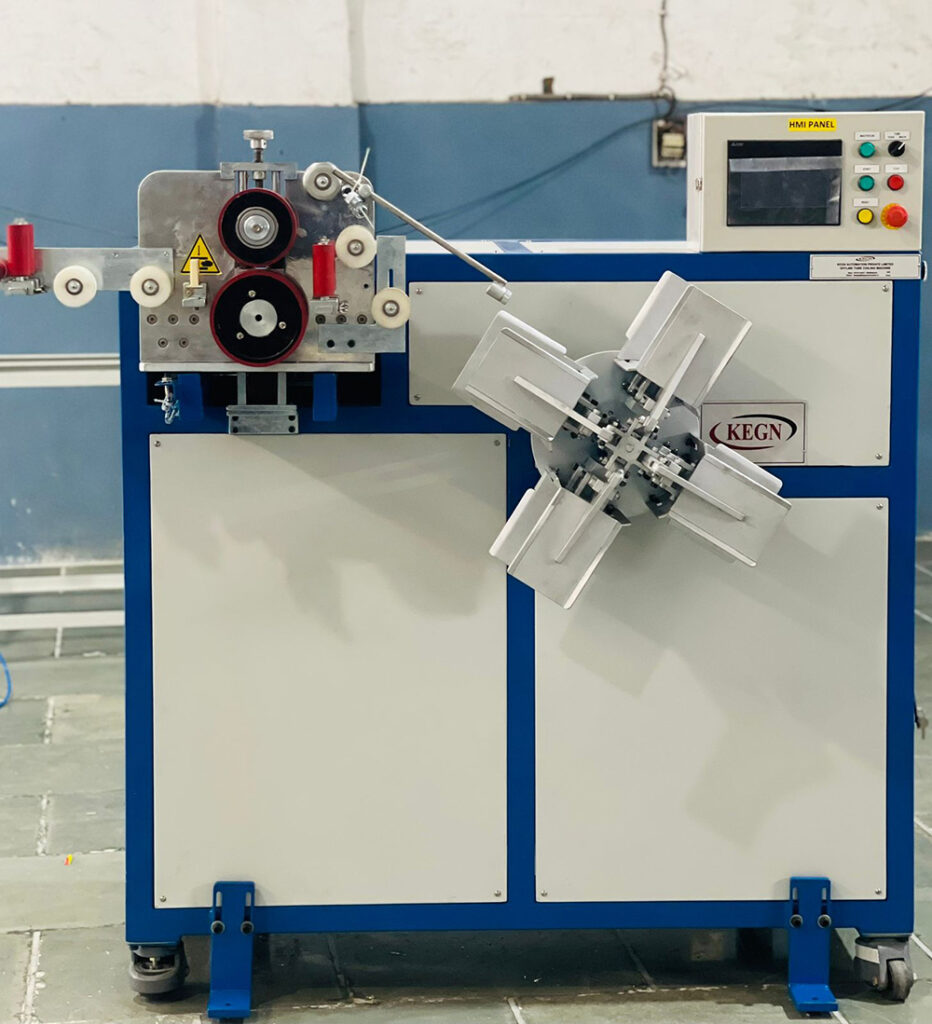
Here’s an overview of the tube bending process:
Tube Selection: Choose a tube or pipe made of a suitable material for bending, considering factors such as strength, ductility, and corrosion resistance. Common materials used include steel, stainless steel, aluminum, copper, and brass.
Tube Preparation: Prepare the tube by removing any burrs, scale, or contaminants from the inside and outside surfaces. This ensures smooth bending and prevents damage to the tube during the process.
Tube Bending Machine Setup: Set up the tube bending machine, which can be manual, hydraulic, or CNC-controlled. The machine consists of a bending die, a clamp die, and a mandrel (optional) to support the tube during bending. Install the appropriate tooling, such as the bending die, clamp die, and mandrel (if required), based on the desired bend radius and tube diameter.
Tube Placement and Fixturing: Position the tube in the bending machine, aligning it with the bending die and clamp die. Use appropriate fixtures or clamps to secure the tube in place, ensuring it remains stable during the bending process.
Tube Bending Process: Activate the bending machine and initiate the bending process. The machine’s bending die exerts force on the tube, causing it to deform and take on the desired shape. The tube can be bent in a single plane (2D bending) or in multiple planes (3D bending) to create more complex shapes.
Mandrel (Optional): In some cases, a mandrel is used to support the inner surface of the tube during bending. The mandrel prevents the tube from collapsing or wrinkling, particularly when bending with a small radius or thin-walled tubes.
